Essential Steps to Take to Protect Your Site from a Hacker

To protect your site from a hacker, you need to lock down your site from the start by realising as a first step that website security is paramount. Hackers constantly evolve, seeking vulnerabilities to exploit. Protecting your website is crucial. This guide outlines proven strategies to secure your site from hacker attacks.
Understanding Website Security
Website security involves safeguarding your site from unauthorized access and data breaches. It ensures the integrity of your data and protects user information. Implementing robust security measures is essential for maintaining trust and credibility.
Importance of Website Security
Hackers can cause significant damage. They steal data, deface websites, and disrupt services. Moreover, a security breach can harm your reputation and lead to financial losses. Therefore, securing your website is not just an option; it’s a necessity.

Essential Security Strategies
Implementing comprehensive security measures can protect your website from potential threats. Here are some key strategies.
Lock Down Your Site by Using HTTPS and SSL Certificates
Secure your site with HTTPS. It encrypts data between the browser and server. Additionally, SSL certificates authenticate your website’s identity. They ensure data integrity and prevent man-in-the-middle attacks.
Implement Content Security Policy (CSP)
A Content Security Policy (CSP) is a powerful tool. It helps prevent cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks. Moreover, CSP restricts resources that can be loaded on your site. This reduces the risk of malicious content execution.
Set a Strict Transport Security Policy
HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS) is crucial. It forces browsers to interact with your site over HTTPS. Furthermore, it prevents protocol downgrade attacks and cookie hijacking. Implementing HSTS enhances your site’s security posture.
Use Referrer Policy
A Referrer Policy controls the information sent in the HTTP referrer header. It protects user privacy and prevents data leakage. For instance, you can restrict referrer data to only your domain. This limits exposure to external sites.
Enable X-Content-Type-Options
The X-Content-Type-Options header prevents MIME type sniffing. It ensures browsers interpret files as declared by the server. This reduces the risk of executing malicious scripts. Another key point is that it strengthens your site’s defence against attacks.
Strengthening Authentication and Access Control
Proper authentication and access control are vital for security. Here are some best practices.
Use Strong Passwords and Multi-Factor Authentication
Weak passwords are an easy target for hackers. Use complex passwords with a mix of characters. Additionally, implement multi-factor authentication (MFA). MFA adds an extra layer of security, requiring a second form of verification.
Lock Down your Site by Limiting Login Attempts
Limiting login attempts can prevent brute force attacks. Set a maximum number of failed login attempts. Moreover, lock accounts after repeated failed attempts. This discourages hackers from attempting to guess passwords. You can install the Limit Login Attempts Reloaded plugin in the WordPress dashboard to do this easily.
Regularly Update Software and Plugins
Outdated software is a common vulnerability. Hackers exploit known flaws in outdated systems. Therefore, regularly update your website’s software and plugins. This ensures you have the latest security patches.
Protecting Against Common Attacks
Understanding common attack vectors helps in implementing effective defences. I highly recommend the Headers Security Advanced & HSTS WP security plugin, which is free and easy to configure. Here are some measures to consider.
Prevent SQL Injection
SQL injection is a prevalent attack method. It involves inserting malicious SQL code into queries. Use parameterized queries and prepared statements to prevent this. Additionally, validate and sanitize user inputs to reduce risks.
Mitigate Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) Attacks
Cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks inject malicious scripts into web pages. Implement CSP to mitigate XSS risks. Furthermore, escape user inputs and use secure coding practices. This prevents scripts from executing in the user’s browser.
Secure File Uploads
File uploads can be a security risk. Hackers may upload malicious files to your server. Validate file types and use virus scanners to check uploads. Moreover, store files outside the web root to prevent direct access.
Here a a screenshot of the security check on my site after installing the Headers Security Advanced & HSTS WP security plugin.
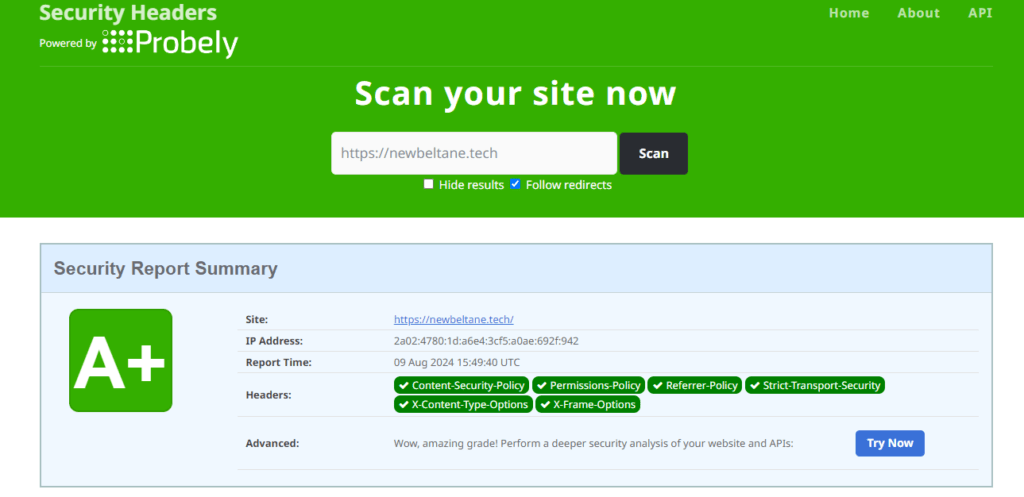
Monitoring and Maintenance
Regular monitoring and maintenance are crucial for ongoing security. Here are some practices to adopt.
Conduct Regular Security Audits
Security audits identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses. Conduct regular audits to assess your site’s security posture. Additionally, use automated tools to scan for vulnerabilities. This helps in promptly addressing any issues.
Implement Web Application Firewalls (WAF)
A Web Application Firewall (WAF) filters and monitors HTTP traffic. It blocks malicious requests and protects against common attacks. Moreover, a WAF can be customised to suit your site’s specific needs.
Backup Your Data Regularly
Regular data backups are essential. In case of a security breach, backups ensure data recovery. Store backups in a secure location and test them periodically. This ensures they are functional and reliable. Most hosting plans offer some form of regular backups of your site. In the cheaper plans this may only be a weekly backup. Hostinger offers a weekly backup in its Premium Plan but daily backups in its Business Plan. Other hosting providers offer similar options.
Alternatively, you can use a WordPress plugin such as Duplicator Pro, which comes with a wealth of options but isn’t free. other plugins include UpdraftPlus, which is free.

Conclusion
Securing your website is an ongoing process. Implementing these strategies can significantly reduce the risk of hacker attacks. Moreover, staying informed about the latest security trends is crucial. By taking proactive measures, you can protect your website and maintain user trust.


